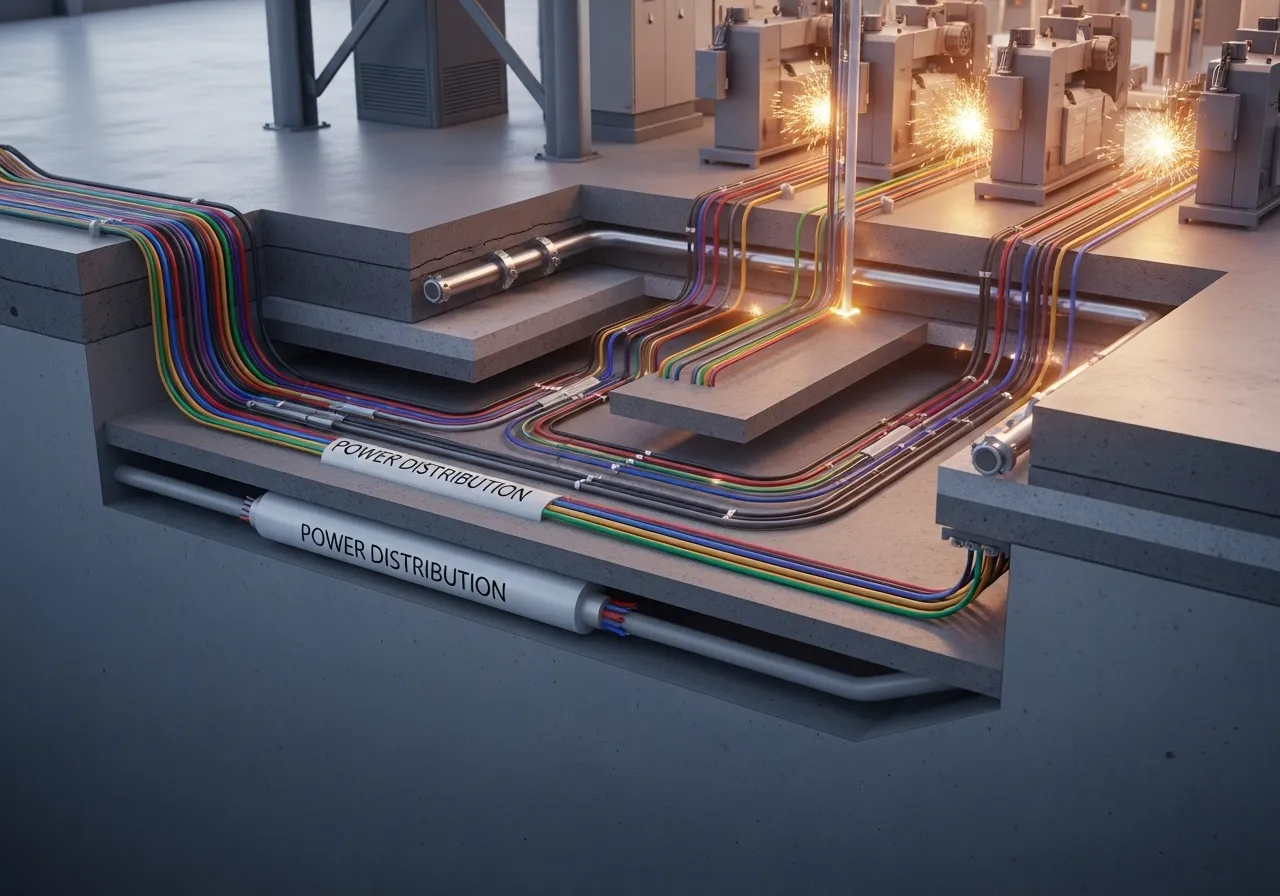
What is a Distribution Line? Electrical Distribution System Structure in Plants for Cooling Towers (MV to LV)

A distribution line for a Cooling Tower is the network that receives electrical power from the source (utility/main switchgear) via the main incomer to the transformer, stepping down from MV LV. It then distributes power to the main bus/feeders, which supply the MCCs for fans, circulation pumps, make-up pumps, basin heaters, and control systems/sensors. If designed and maintained correctly, the system will start smoothly, reduce voltage sags during startup, minimize nuisance trips, and prevent damage to critical equipment like fan gearboxes, VFDs, and motor bearings, while also reducing safety risks for operators.
Key Equipment for "Stable and Safe" Power
The core of the line is switchgear and protection devices (ACB/MCCB/Fuse), working with transformers, busways/cables, MCCs, and auxiliary equipment like capacitor banks/active filters/UPS for critical controls. In systems using VFDs (inverters) for fan speed control, proper harmonic filters and grounding are essential to maintain power quality and extend motor insulation life.
Key Items in a Line:
- Main Incomer + Switchgear: The main point of reception, isolation, and protection, with protective relays.
- Transformer + Busway/Cable: Efficiently distributes power to the fan/pump MCCs.
- ACB/MCCB/Fuse: Protects against overload/short circuits, isolating only the faulty section.
- Protection Relay: Monitors for ground faults, overcurrents, or differentials to prevent major damage.
- Auxiliary Equipment: Capacitor bank, active filter, UPS, surge protection for control circuits.
Protection Coordination: Preventing "Domino" Trips in the Cooling Tower
The heart of a reliable system is ensuring the "device closest to the fault" trips first. This is achieved by setting TimeCurrent Curves (TCCs) so they don't overlap, allowing for the inrush of fan/pump motors and switching transients. Settings must be based on actual operational data, such as start cycles, start method (DOL/Soft starter/VFD), and the start sequence of fans/pumps, to prevent an upstream main from tripping before the downstream device, which would cause an unnecessary tower-wide shutdown.
Power Quality: A Factor to Consider from the Design Phase
Cooling Towers often have multiple medium-to-large motor loads that may start closely together, causing voltage sags that affect controls, sensors, and electric valves. Using VFDs reduces inrush but introduces harmonics. The solution is to design Active/Passive filters corresponding to the number and size of VFDs and ensure proper grounding/shielding to reduce EMI/RFI feeding back into signal circuits. Meanwhile, detuned capacitor banks should be considered to avoid resonance with the line's dominant harmonics.
Example Parameters to Consider:
- Transformer/bus sizing and voltage drop during multi-motor starts.
- Ratio of VFDs to total load and the expected THDi/THDv levels.
- Starting method/sequence for fans and pumps to minimize simultaneous inrush.
- Protection for control circuits (UPS, surge/EMI filters) for continuous operation.
- Arc-flash ratings and safety boundaries for maintenance work.
Architecture for High Availability (Reliability)
Plants operating 24/7 should consider Dual feeders/Loops for the main bus, separating the fan MCC from the pump MCC to reduce cross-impact, and designing bypasses for maintenance without a full shutdown. In the control system, redundant I/O for critical signals (e.g., basin level, flow switch, vibration switch) helps the system shut down safely rather than suddenly.
Preventive Maintenance: How to Keep Power "Stable" for the Long Term
Beyond routine cleaning and tightening, performing Thermography to find hot spots on connections/busbars, Insulation resistance tests on cables/motors, and functional testing of relays/breakers per the manufacturer's guide, along with updating as-built drawings, significantly reduces unexpected events. Logging trip/sag events with corresponding weather/load data allows engineers to see patterns and adjust settings accurately.
Periodic PM Checklist:
- Thermal scan of main panels, buses, and cable terminations; clean dust/chemical residue.
- Test ACB/MCCB/Relay functions and update TCC settings.
- Check THD levels and review the performance of filters/Cap banks.
- Megger test insulation for fan/pump motors and cables; check terminal tightness.
- Review Arc-flash labels/PPE and conduct LOTO training for the team.
Summary: Stable Power = Smooth Fans/Pumps = Process Stability
A systematically designed and maintained distribution line ensures the Cooling Tower runs smoothly, reduces inrush current, minimizes the chance of domino trips, and extends the life of all equipment in the chainfrom the main incomer to the fan bladestranslating into stability for the entire production process.