What is a Heat Exchanger? Principles, Types, and Selection Guide
In industries related to energy, chemicals, food, and air conditioning, the heat exchanger is indispensable. It is a crucial component that facilitates heat transfer between two fluids without them coming into direct contact. Understanding its working principles and proper selection can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and extend the system's lifespan.
What is a Heat Exchanger?
A Heat Exchanger is a device used to transfer thermal energy from one fluid to another without the two fluids mixing. Examples include cooling water and steam, or refrigerant and air. This process helps regulate the system's temperature for optimal operation.
Working Principle of a Heat Exchanger
The fundamental principle is "heat transfer." A fluid with a higher temperature transfers its energy to a fluid with a lower temperature through the walls of tubes or plates. This process depends on the transfer area and the properties of the material used.
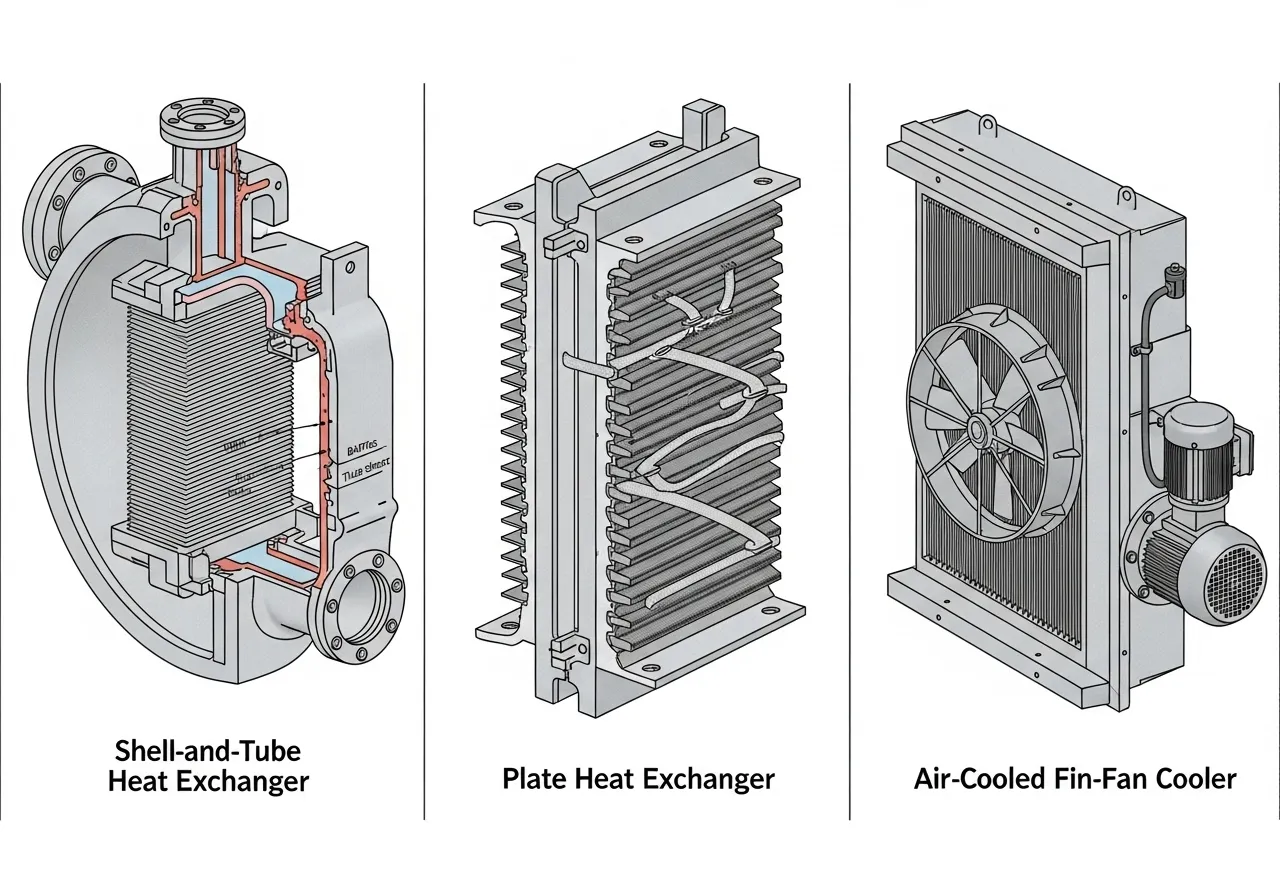
Types of Heat Exchangers
In the industrial sector, heat exchangers are designed in various forms depending on the application, such as:
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger: Commonly used in chemical plants and power stations; robust and can handle high pressure.
- Plate Heat Exchanger: Uses thin metal plates stacked together, ideal for applications requiring a large heat transfer area in a compact size.
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger: Uses air for cooling, eliminating the need for water, suitable for areas with water scarcity.
- Double Pipe Heat Exchanger: Features a simple structure, used for small to medium-sized applications.
- Fin Fan Cooler: Emphasizes the use of fans for cooling, often used in the oil and gas industry.
Benefits of a Heat Exchanger
Installing a heat exchanger allows a system to operate continuously, safely, and more cost-effectively.
- Controls temperature in the production process.
- Saves energy by recovering and reusing heat.
- Extends the lifespan of equipment and machinery.
- Prevents damage from excessive or insufficient heat.
- Supports safety standards in industrial plants.
How to Choose the Right Heat Exchanger
Selection must consider several factors, such as:
- Type of fluids (water, oil, gas, steam).
- Operating temperature and pressure.
- Installation space and size constraints.
- Investment and maintenance budget.
- Service life and corrosion-resistant materials.
Conclusion
It is evident that heat exchangers play a vital role in various industries. Understanding their working principles, types, and selection criteria helps organizations improve efficiency, reduce costs, and build safer systems.