What is a CLOSED LOOP COOLING TOWER? Understanding Closed-System Cooling
In industrial applications or systems requiring heat dissipation, the circulating water affects the efficiency and lifespan of machinery. The CLOSED LOOP COOLING TOWER, or "closed-circuit cooling tower," was developed to reduce contamination and control water quality more effectively than traditional open systems.
What is a CLOSED LOOP COOLING TOWER?
A CLOSED LOOP COOLING TOWER is a cooling tower where the cooling water circulates in a closed pipe system, without direct contact with the outside air. This cooling water transfers heat through the pipe walls to spray water or air that passes over them, reducing the chance of contamination from dust, scale, or microorganisms. In other words, the primary water used for cooling maintains a near-original quality even with continuous use.
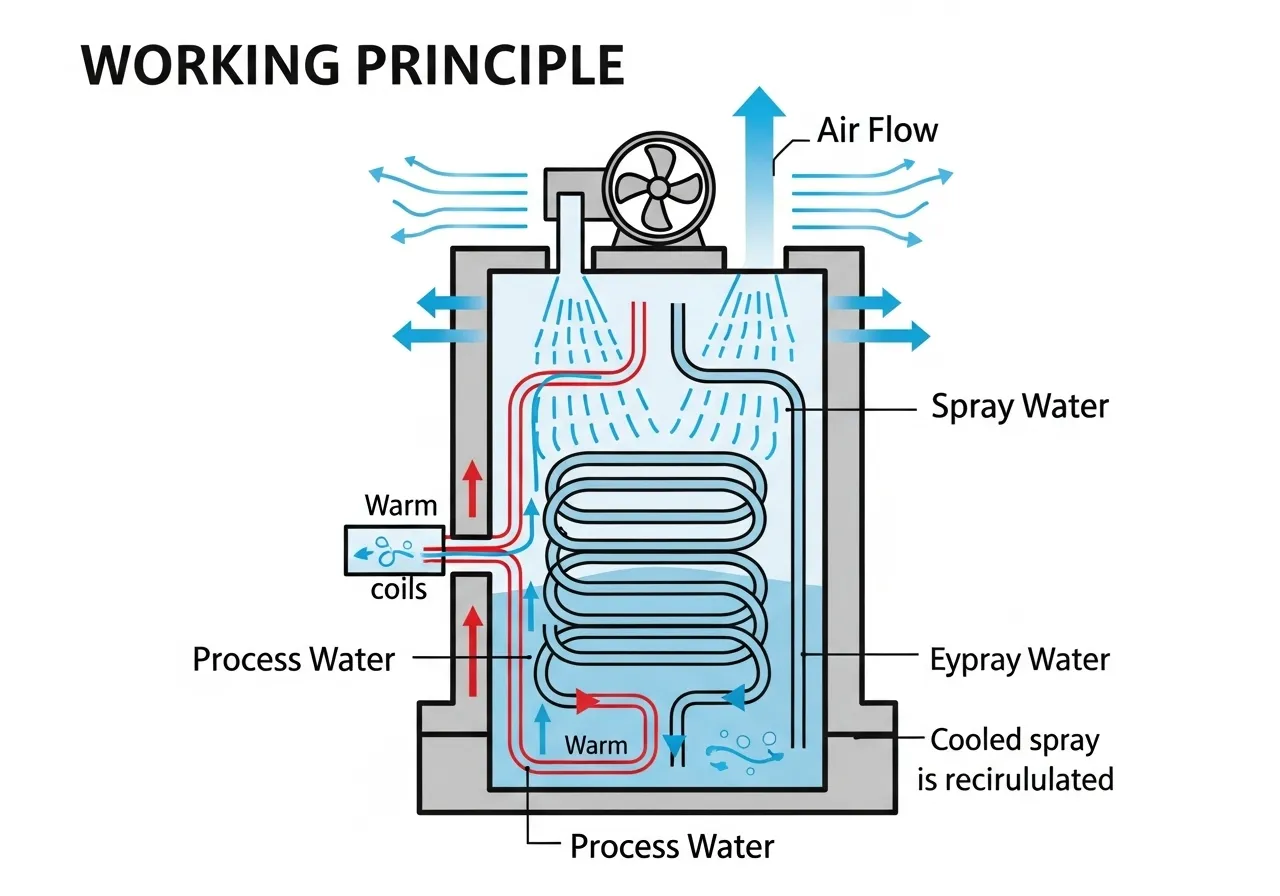
Working Principle of the Closed System
The operation of this system can be described in steps:
- The primary cooling water (Process Water) flows within a sealed coil.
- A pump delivers secondary water (Spray Water) onto the coil's surface to extract heat.
- A fan helps to continuously cool the secondary water.
- The primary cooling water is then returned to the application with its quality preserved.
By separating the primary cooling water from the air, the closed system can maintain water cleanliness and stability better than an open system.
Advantages and Limitations of the Closed System
Closed systems are becoming increasingly popular due to several advantages, such as keeping water clean, preventing contamination, and reducing maintenance loads. The main points are as follows:
- Stable Water Quality: Reduces the accumulation of scale, dust, and dirt.
- Reduced Contamination: The water in the pipes does not come into direct contact with air, lowering the risk of bacteria or biofilm formation.
- Easy Maintenance: Does not require cleaning as frequently as open systems.
- Suitable for Critical Applications: Ideal for industries like electronics, pharmaceuticals, or chiller systems that require high cleanliness.
However, limitations to consider include a higher installation cost, the need to maintain the secondary water that is exposed to air, and potentially larger space requirements for some models.
CLOSED LOOP vs OPEN LOOP
When compared to an open system, it is clear that an Open Loop system cools directly as water contacts the air, making it cool faster but also degrade easily. A Closed Loop system, despite its higher initial investment, provides stable water quality and a longer lifespan for the machinery.
Industrial Applications
Closed systems are often chosen for applications where water quality is critical, such as electronics manufacturing, chiller systems, food and drug factories, or power plants that require high stability. Using an open system in these contexts could lead to contamination and a higher risk of damage.
Conclusion
A CLOSED LOOP COOLING TOWER is a cooling solution that meets the demands of modern industry, focusing on stable water quality and reduced contamination. Although the initial cost is high, when considering the long-term value in terms of maintenance and extended equipment life, it is a suitable choice for organizations seeking long-term efficiency and safety.